Noteworthy Names: The Top 10 Blackfoot People You Should Know
Blackfoot, also known as Siksika, is a Native American tribe from the Great Plains region. Over the years, several notable people from Blackfoot ethnicity have made their mark in various fields, including entertainment, sports, and activism. Here are 10 popular celebrities and notable people from Blackfoot ethnicity:
- Graham Greene: Graham Greene is a renowned Canadian actor who has appeared in numerous films and TV shows. He is of both Oneida and Blackfoot heritage.
- Natasha Kanapé Fontaine: Natasha Kanapé Fontaine is a prominent poet, actress, and activist from Blackfoot descent. Her powerful works focus on Indigenous rights and culture.
- Tantoo Cardinal: Tantoo Cardinal is a highly respected Canadian actress of Métis and Blackfoot origin. She has appeared in several notable films and TV shows.
- Tommy Lee Cook: Tommy Lee Cook is a former professional football player who played in the NFL. He is of Blackfoot ancestry.
- Jemaine One Eagle: Jemaine One Eagle is a notable Blackfoot artist known for his beautiful paintings and intricate beadwork. He is recognized for his contributions to Indigenous art.
- Wilton Littlechild: Wilton Littlechild is a prominent Blackfoot lawyer, politician, and former Grand Chief of the Confederacy of Treaty Six First Nations. He has been a strong advocate for Indigenous rights.
- Ada E. Deer: Ada E. Deer is an influential Native American activist, scholar, and politician from the Menominee and Blackfoot tribes. She has made significant contributions to Native American policy.
- Jesse Collings: Jesse Collings is a talented Blackfoot sculptor known for his remarkable woodcarvings and stone sculptures. His works reflect Blackfoot culture and spirituality.
- Lakota Harden: Lakota Harden is an activist, writer, and filmmaker who has been involved in social justice movements for over four decades. She is of Blackfoot and Lakota ancestry.
- Geri Small: Geri Small is a renowned Blackfoot artist and activist who uses her art to promote Indigenous culture and raise awareness about social and environmental issues.
These individuals have played significant roles in promoting and preserving Blackfoot culture while achieving personal success in their respective fields. Their contributions continue to inspire and empower both their community and the wider world.
Most Famous Blackfoot People
Blackfoot’s Three Pinnacle Historical Inheritances
The Blackfoot community is a Native American tribe that is located in the Great Plains region of North America. They are known for their rich cultural heritage, which has been passed down from generation to generation. Here are three of the most well-known historical inheritances associated with the Blackfoot heritage:
- Traditional Beliefs: The Blackfoot people have a strong belief in the spirituality of the natural world. They believe that everything in the world has a spirit and that it is important to maintain a harmonious relationship with nature. For them, the land, water, animals, and plants are all revered as sacred and deserving of respect. This belief system has guided their way of life, influencing their hunting practices, ceremonies, and rituals.
- Bison Hunting Culture: One of the most iconic aspects of the Blackfoot heritage is their bison hunting culture. Historically, the Blackfoot people were highly skilled buffalo hunters and relied on the bison for their survival. They would organize large-scale communal hunts, where they would strategically drive herds of buffalo off cliffs or into carefully constructed corrals. The bison provided them with food, clothing, and materials for their dwellings. This hunting culture played a significant role in shaping their societal structure and cultural practices.
- Warrior Traditions: The Blackfoot people were renowned warriors, known for their bravery and skill in battle. They had a strong warrior tradition and engaged in conflicts with neighboring tribes as well as white settlers. The Blackfoot warriors were known for their distinct fighting style, which involved fierce hand-to-hand combat and the use of weapons like bows and arrows, spears, and war clubs. They also had a rich oral tradition of storytelling, where warriors would share tales of their heroic exploits in battle.
The Blackfoot community has a proud and vibrant heritage that continues to be celebrated today. Their traditional beliefs, bison hunting culture, and warrior traditions are just a few examples of the historical inheritances that have shaped the identity of the Blackfoot people and continue to be treasured within the community.
Factsheet About Blackfoot People
| Demographics | Blackfoot |
|---|---|
| Population | Approximately 25,000 |
| Region | Alberta, Canada |
| Main Tribe | Siksika Nation |
| Language | Blackfoot |
| Traditional Territory | Alberta, Saskatchewan, Montana |
| Religion | Traditional Indigenous Spirituality, Christianity |
| Socioeconomic Status | Varies, many face socio-economic challenges |

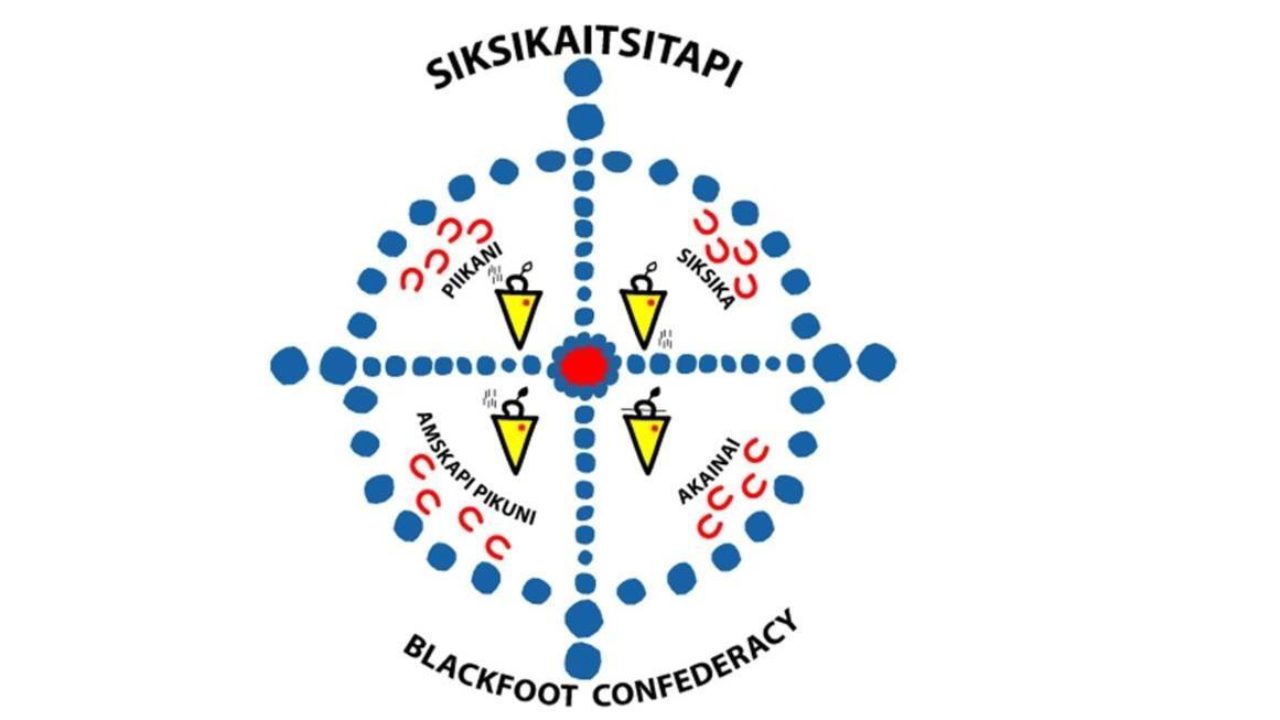
The Ancient Heritage of Blackfoot Ethnic Groups
Blackfoot Ethnicity: References and Resources
For those looking to dig deeper into the Blackfoot ethnic group, there are several resources available that provide valuable insights into their history, culture, and traditions. Here are some references and materials to explore:
- “The Blackfoot People” by Donald B. Smith: This book offers a comprehensive overview of the Blackfoot people, their history, customs, and contemporary issues. It delves into their way of life, spirituality, and interactions with European settlers.
- “The Blackfoot Dictionary of Stems, Roots, and Affixes” by Donald G. Frantz and Norma Jean Russell: A linguistic resource that explores the Blackfoot language, this dictionary is a valuable tool for studying the structure, vocabulary, and syntax of the Blackfoot language.
- “Blackfoot Ways of Knowing: The Worldview of the Siksikaitsitapi” edited by Betty Bastien: This anthology brings together various authors who share insights into Blackfoot traditional knowledge, worldview, teachings, and stories. It provides a deeper understanding of their cultural beliefs and values.
- “When Buffalo Ran: Blackfoot Recollections of the Northwest Rebellion” by Hugh A. Dempsey: This book offers firsthand accounts and narratives from Blackfoot individuals who witnessed the Northwest Rebellion and its impact on their communities. It provides a unique perspective on this historical event.
- “Voices of the Plains Cree, Blackfoot, and Sioux: Native Peoples’ Experiences of the Western Canadian Plains from the 1870s to the 1930s” by Julie Cruikshank: This work explores the oral histories and life narratives of Blackfoot individuals, shedding light on their experiences during a critical period of colonial encroachment and cultural change.
These resources provide a starting point for deeper exploration of the Blackfoot ethnic group. Whether you are interested in their history, language, worldview, or personal narratives, these references will help you gain a richer understanding of the Blackfoot people and their cultural heritage.
Explore other famous people with Amish, Ainu, and Anglo American roots, showcasing the diversity of ethnic backgrounds. Exploring notable figures from diverse ethnic backgrounds related to these Blackfoot roots provides insight into the interconnectedness of global cultures and their contributions to the world.

